
This makes commutated motors unsuitable for low particulate or sealed applications like hard disk motors, and for applications that require maintenance-free operation.
It consists of a rotating cylinder divided into multiple metal contact segments on the rotor.

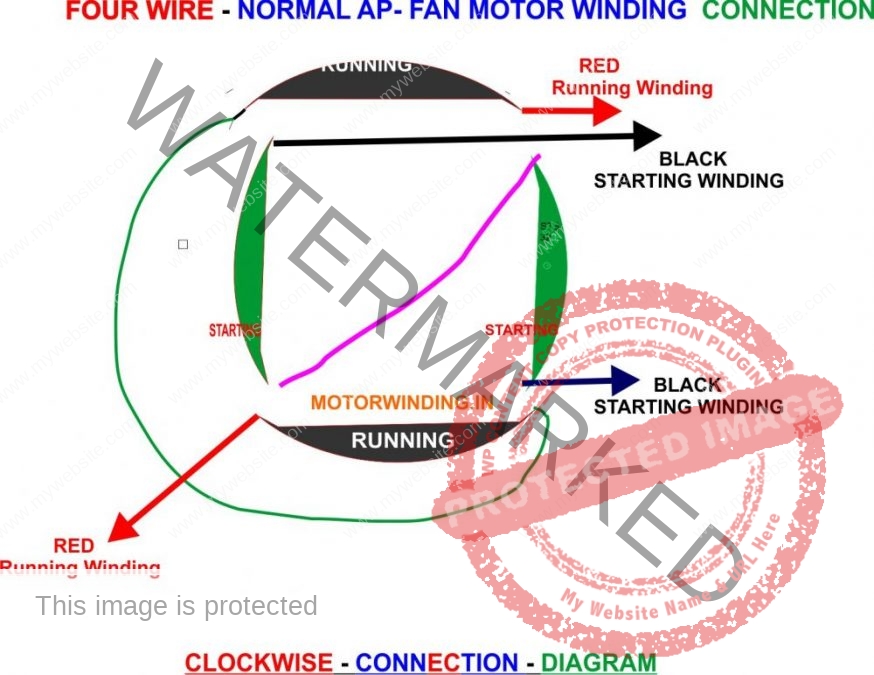
In brushed motors this is done with a rotary switch on the motor's shaft called a commutator. The device that moves the fields based on the position of the rotor is called a commutator. As the rotor moves, and the fields come into alignment, it is necessary to move either the rotor's or stator's field to maintain the misalignment and continue to generate torque and movement. The misalignment generates a torque that tries to realign the fields. DC running through the wire winding creates the magnetic field, providing the power which runs the motor. One or both sets of magnets are electromagnets, made of a coil of wire wound around an iron core. Īn electric motor develops torque by keeping the magnetic fields of the rotor (the rotating part of the machine) and the stator (the fixed part of the machine) misaligned. Brushless DC motors were made possible by the development of solid state electronics in the 1960s. In modern washing machines, brushless DC motors have allowed replacement of rubber belts and gearboxes by a direct-drive design.īrushed DC motors were invented in the 19th century and are still common. Brushless motors find applications in such places as computer peripherals (disk drives, printers), hand-held power tools, and vehicles ranging from model aircraft to automobiles. The advantages of a brushless motor over brushed motors are high power-to-weight ratio, high speed, nearly instantaneous control of speed (rpm) and torque, high efficiency, and low maintenance. They may also use neodymium magnets and be outrunners (the stator is surrounded by the rotor), inrunners (the rotor is surrounded by the stator), or axial (the rotor and stator are flat and parallel). The construction of a brushless motor system is typically similar to a permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM), but can also be a switched reluctance motor, or an induction (asynchronous) motor. This control system is an alternative to the mechanical commutator (brushes) used in many conventional electric motors. The controller adjusts the phase and amplitude of the DC current pulses to control the speed and torque of the motor.

It uses an electronic closed loop controller to switch DC currents to the motor windings producing magnetic fields which effectively rotate in space and which the permanent magnet rotor follows. The two coils on the printed circuit board interact with six round permanent magnets in the fan assembly.Ī brushless DC electric motor ( BLDC motor or BL motor), also known as an electronically commutated motor ( ECM or EC motor) or synchronous DC motor, is a synchronous motor using a direct current (DC) electric power supply.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
